
Every day, hackers are looking for —and finding — vulnerabilities in secure networks and applications. Most of these vulnerabilities can be eliminated by applying patches or fixed, but by some accounts, there are as many as seven critical patches released every day. For a busy security IT team, immediately applying those patches to every server is a cumbersome, and sometimes impossible, task. Compounding the problem is the shift to virtual environments. Traditional security and patching methods are not effective in the virtual environment for various reasons, meaning that without an effective solution, performance issues and security holes will remain, leaving your networks and data vulnerable to theft. One of the best solutions to the issue of managing security patches is virtual patching. This agentless solution immediately identifies security vulnerabilities and applies necessary fixes, creating a secure environment until the critical or “official” patch can be applied. Such a system overcomes many of the issues presented by virtual environments as well, preventing a serious and costly data breach as a result of poor patch management.
One of the best solutions to the issue of managing security patches is virtual patching. This agentless solution immediately identifies security vulnerabilities and applies necessary fixes, creating a secure environment until the critical or “official” patch can be applied. Such a system overcomes many of the issues presented by virtual environments as well, preventing a serious and costly data breach as a result of poor patch management.
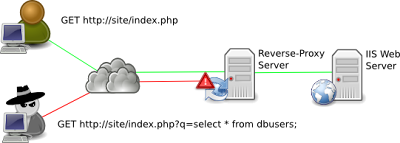
Where You’re Vulnerable and Why In most enterprises, there are several places where vulnerabilities can be found. For example, you may be running an older operating system or application the developer no longer supports or issues patches for, and your security measures will not protect those systems. Other issues include systems that cannot be shut down to apply patches for fear of lost productivity or revenue, delayed release of patches and fixes from the developer and SQL injection attacks via Web applications that can be difficult to locate and fix on a large scale.
The virtual environment only complicates these vulnerabilities. Under a traditional security model, all of the traffic from virtual machines must flow through one central server to be scanned for malicious content or code, which causes network congestion and slows down network performance. Compounding the problem is the fact that in many virtual environments, the server locations regularly move, turn on and off according to demand or are dormant for extended periods. This all makes it difficult to consistently and effectively apply patches as needed. How Virtual Patching Works While correcting the source code of the vulnerability via a patch is the ideal re-mediation strategy for any potential problem, that’s not always practical.
This is where virtual patching comes in. Technically speaking, a virtual patch is an additional layer of virtualization security that prevents hackers from taking advantage of a known security vulnerability. Again, because vulnerabilities quickly change, it can be all but impossible to effectively apply every new patch as it’s released, and a system that was completely impervious one day could be ripe for an attack the next. That’s why some people call virtual patching “just in time” patching or “external patching,” because it blocks vulnerabilities before they become problems. Regardless of terminology, it provides an important layer of protection against a potentially devastating security breach. Virtual patching relies on intrusion protection and detection (IPS/IDS) rules to protect against known vulnerabilities, including those that have not yet been addressed by patches.
The advanced network security system automatically scans the network to determine the OS, applications in use, patches that have already been deployed and other factors, and determines which rules need to be activated to protect the system. As things change — new patches are installed,for example —
the virtual patching system will automatically adjust the IPS/IDS rules that apply, so as to avoid service disruptions and system slowdowns. In the virtual environment, such a patching system covers all virtual machines —including new machines and those that have been dormant — and routes all traffic through a secure machine to ensure protection on every front. Patch management is one of the most important — and most time-consuming — tasks for many IT security teams. In fact, some surveys indicate these tasks take up the majority of their time, but are largely ineffective.
For those organization struggling with patch management, or even those who have a handle on it but need to ensure compliance and data integrity, virtual patching is an ideal solution, adding a layer of protection that traditional perimeter security measures simply cannot.
source : http://www.securitygeeks.net
Where You’re Vulnerable and Why In most enterprises, there are several places where vulnerabilities can be found. For example, you may be running an older operating system or application the developer no longer supports or issues patches for, and your security measures will not protect those systems. Other issues include systems that cannot be shut down to apply patches for fear of lost productivity or revenue, delayed release of patches and fixes from the developer and SQL injection attacks via Web applications that can be difficult to locate and fix on a large scale.
The virtual environment only complicates these vulnerabilities. Under a traditional security model, all of the traffic from virtual machines must flow through one central server to be scanned for malicious content or code, which causes network congestion and slows down network performance. Compounding the problem is the fact that in many virtual environments, the server locations regularly move, turn on and off according to demand or are dormant for extended periods. This all makes it difficult to consistently and effectively apply patches as needed. How Virtual Patching Works While correcting the source code of the vulnerability via a patch is the ideal re-mediation strategy for any potential problem, that’s not always practical.
This is where virtual patching comes in. Technically speaking, a virtual patch is an additional layer of virtualization security that prevents hackers from taking advantage of a known security vulnerability. Again, because vulnerabilities quickly change, it can be all but impossible to effectively apply every new patch as it’s released, and a system that was completely impervious one day could be ripe for an attack the next. That’s why some people call virtual patching “just in time” patching or “external patching,” because it blocks vulnerabilities before they become problems. Regardless of terminology, it provides an important layer of protection against a potentially devastating security breach. Virtual patching relies on intrusion protection and detection (IPS/IDS) rules to protect against known vulnerabilities, including those that have not yet been addressed by patches.
The advanced network security system automatically scans the network to determine the OS, applications in use, patches that have already been deployed and other factors, and determines which rules need to be activated to protect the system. As things change — new patches are installed,for example —
the virtual patching system will automatically adjust the IPS/IDS rules that apply, so as to avoid service disruptions and system slowdowns. In the virtual environment, such a patching system covers all virtual machines —including new machines and those that have been dormant — and routes all traffic through a secure machine to ensure protection on every front. Patch management is one of the most important — and most time-consuming — tasks for many IT security teams. In fact, some surveys indicate these tasks take up the majority of their time, but are largely ineffective.
For those organization struggling with patch management, or even those who have a handle on it but need to ensure compliance and data integrity, virtual patching is an ideal solution, adding a layer of protection that traditional perimeter security measures simply cannot.
source : http://www.securitygeeks.net
















0 comments:
Post a Comment